Explore the Life Cycle Analysis of Overhead Lines
The Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) presentation is a comprehensive exploration of the environmental, economic, and social impacts associated with overhead transmission lines. This two-hour session focuses on the comparison between ACSR GZ and AAAC 1120 round wire conductors: Lemon vs. Nitrogen and Orange vs. Selenium. Additionally, insights into the use of High Temperature Low Sag (HTLS) compared to compact AAAC 1120 designs are discussed.
To book a face to face or online presentation of this important topic contact Michael LEE
Line losses over the life of the overhead conductor are significant!
This page highlights featured readings associated with the online or face to face course. The CIGRE Technical Brochures are available to CIGRE members, the other featured readings are open access documents.
Reading 1: Life Cycle Modelling of Extraction Processing of Battery Minerals
The study employs a parametric attributional process-based life cycle model to assess the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from the value chains of six raw battery materials: aluminum, copper, graphite, lithium carbonate, manganese, and nickel. This model is designed to explore the impact of various 'levers' (factors affecting emissions) within these value chains. The researchers conducted numerous distinct life cycle assessments (LCAs) for each material, varying the identified levers within defined engineering ranges to generate a spectrum of possible emissions outcomes. The results are presented as three-dimensional contour plots illustrating the intensity of lever combinations on GHG emissions.
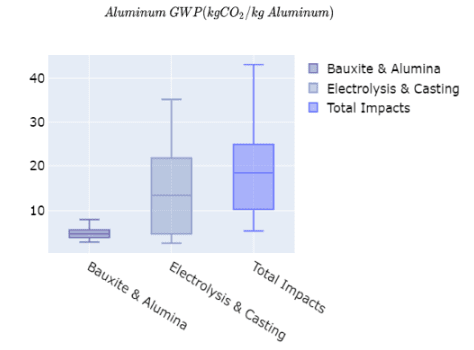
The main findings that we are interested in are with the Aluminum and Copper Value Chains: The study identifies crucial factors in the aluminum and copper value chains that significantly influence their GHG emissions. For aluminum, these include ore grades, alumina recovery efficiency, and electricity mix's carbon intensity. In the case of copper, ore grade, beneficiation recovery, electricity mix intensity, recovery efficiency, and smelting technology are identified as significant influencers.
Reading 2: Reducing the Carbon Footprint: Primary Production of Aluminium and Silicon with Changing Energy Systems
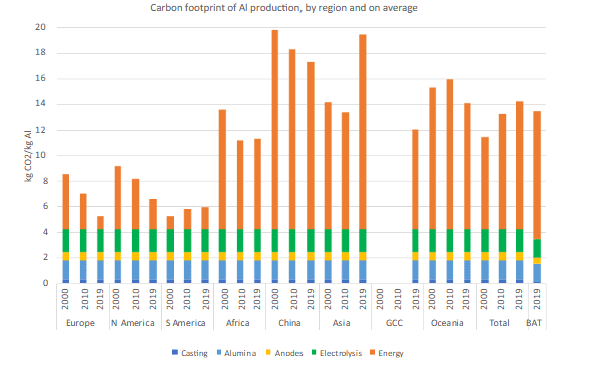
The article discusses strategies and methodologies for reducing the carbon footprint in the primary production of aluminum and silicon, particularly in the context of evolving energy systems. This is a significant area of research due to the high energy requirements and environmental impacts associated with the production of these materials.
Aluminum production is traditionally energy-intensive, primarily using the Hall-Héroult process, which involves electrolysis of alumina dissolved in molten cryolite. This process is a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions, especially when the electricity used is derived from fossil fuels.
Reading 3: Electricity Grids and Secure Energy Transitions: Enhancing the Foundations of Resilient, Sustainable and Affordable Power Systems
The document examines the challenges and opportunities associated with modernizing electricity grids to support the transition to more sustainable, resilient, and affordable energy systems. This transition is crucial in the context of global efforts to combat climate change, increase energy security, and promote economic development. The IEA documents are good general reading for the Life Cycle Analysis of the value chain assciated with overhead conductors.
Reading 4: Life Cycle Assessement on a 765kV AC transmission system
Available to CIGRE members via e-cigre
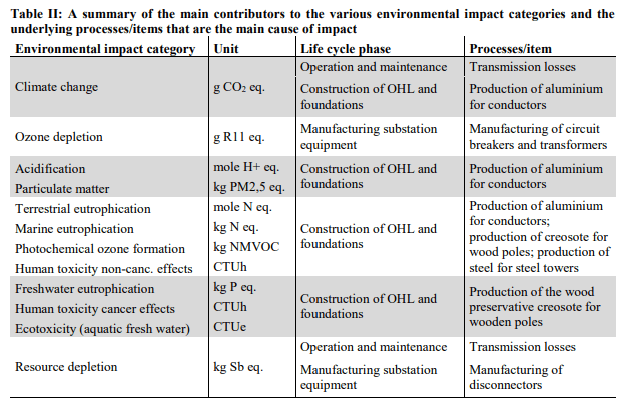
This session paper examines in detail a full system (from materials of construction, use and disposal) and includes transmission lines, structures, transformers, substations and fittings for a 760km long line in Venezuala.
After investigation it’s revealed that the energy losses in transmission lines is the dominating environmental impact in use phase, which is roughly 10 times of that of energy losses in substations, and 3.5 times of that of circuit breakers’ SF6 emissions’ Global Warming impact.
Reading 5: Life Cycle Assessement of the high voltage OHL transmission system in Iceland
Available to CIGRE members via e-cigre
Some of the key findings in this symposium paper are:
Environmental Impacts: The study identifies the main environmental impacts as stemming from infrastructure and transmission losses. Manufacturing of aluminium (for conductors) and steel (for towers) are significant contributors across various impact categories, while transmission losses predominantly affect climate change impacts.
Carbon Footprint: The carbon footprint of transmitting 1 kWh of electricity in the system is 0.64 g CO2 eq./kWh, with transmission losses accounting for 57% of this footprint. This emphasizes the critical role of transmission efficiency and the energy source in determining the environmental performance of transmission systems.
CIGRE TB265
Available to CIGRE members via e-cigre
"Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) for Overhead Lines" by the CIGRE Working Group B2.15, published in December 2004, offers a comprehensive evaluation of the environmental impacts associated with overhead power lines.
The Technical Brochure is fairly general in nature (2000 working group initiated; 2004 publish date) however, it does examine LCA issues as applied to Overhead Lines, focusing on environmental concerns.
* It outlines the development of LCA, its early applications, and its current applications, particularly in the electrical industry.
* The document details the general structure of the ISO 14040 series, covering aspects like goal definition, overhead lines applications, and scope of study.
* Examples are provided - Denmark, Sweden; 154 and 400kV and serve as a basis for more detailed studies today
CIGRE TB635
Availble to CIGRE members via e-cigre
"Microgrids 1: Engineering, Economics, & Experience" by CIGRE Working Group C6.22, published in October 2015, provides an extensive analysis of microgrids from various perspectives, including engineering, economic, and practical experiences.
The brochure covers key elements for developing and implementing viable microgrids, including business cases, technology configuration, and interaction with the electric power system. It lays out the groundwork for microgrid concepts, types, and scopes.
CIGRE TB748
Availble to CIGRE members via e-cigre
"Environmental Issues of High Voltage Transmission Lines in Urban and Rural Areas," prepared by CIGRE Working Group C3/B1/B2, addresses the various environmental concerns associated with high voltage overhead lines (HV OHLs).
The technical brochure sets the context for the environmental challenges posed by HV OHLs in both urban and rural settings. It aims to inform a broad audience, including non-technical readers, about electricity utilities' policies and practices globally.
The report discusses the contentious nature of routing HV OHLs near homes, developments, and sensitive natural areas. It highlights public concerns over electromagnetic fields (EMF), visual impacts, and property value loss. The document aims to provide a global perspective on utilities' policies and government controls in this area.
Line losses are not discussed in detail.
Connect for Expert Training
Life Cycle Analysis of overhead lines provides a comprehensive perspective on the environmental impact of these critical infrastructure components, guiding decision-makers toward more sustainable practices in the design, construction, operation, and decommissioning phases. Reach out to us if you are looking for expert training focused on overhead line conductors.